Introduction into AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands out as one of the swiftest expanding and widely discussed technologies. The current global AI market, valued at more than $136 billion, is expected to surge significantly, predicted to grow more than 13-fold over the next seven years, reaching a staggering $299.64 billion by 2026. This growth trajectory is set to continue with an impressive compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38.1% through 2030.
Why is AI so desirable? AI is changing every type of business by better and faster decision-making. It operates predictive models, provides rationale for quick decision making. AI considers vast amount of feedback, customer reviews that previously were hard to be analyzed and could transform the business notwithstanding the industry specifics or the size.
The AI types are going from the easiest and least costly to the most complex solutions:
- Cognitive computing processes the inserted data but does not make any human-like conclusions. It’s frequently used in data analysis and the ‘cheapest’ solution to adopt.
- Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence that enables computers to interpret and understand visual information from the world, similar to how humans perceive and analyze images and videos.
- Deep learning uses existing external neural networks with multiple layers (deep neural networks) to process and learn from data, enabling the model to automatically extract intricate features and patterns from complex datasets.

Figure 1. Key characteristics of AI types (1/2)
- Neural network is a computational model inspired by the structure and functioning of the human brain. It learns patterns and relationships within data through training.
- Generative AI involves creating or generating new content, such as images, text, music, or even entire scenarios, using algorithms and models. It is based on limited data pools and learning processes of GAI are very expensive and time-consuming.
- Machine Learning encompasses various techniques for recognizing patterns, making predictions, and generating insights from large datasets. It requires huge amount of well-prepared data.

Figure 2. Key characteristics of AI types (2/2)
The primary focus of AI usage is to streamline routine tasks and improve business efficiency. Companies should clearly understand why they need AI, and what result they want to get with its help. It is crucial for each company to define the business goals and to understand AI’s capabilities in this direction. AI has already gained reputation to increase business productivity, to bring economic benefits and to be instrumental for customer reach and more profitability, according to the recent surveys.
Industry landscape
Adoption of AI is not homogenous within industries. Data-reliant industries – banking, healthcare, telecom, media – have long been processing Big Data, which has become a good foundation for AI products, and these industries have been running fierce competition with their solutions.
There are 4 clusters of industries depending on level of AI adoption and diversity of its usage (Strong and early digital adopters, heavy AI adopters, Moderate AI adopters and Laggards).
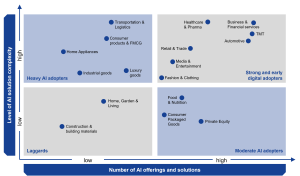
Figure 3. Industry landscape in terms of AI footprint
- Strong and early digital adopters are pioneers in developing and creating AI solutions. Their business strategy is fundamentally connected to AI in all types of operations. The range of use-cases is the widest among the clusters.
- Moderate AI adopters seek transparency to enhance their information-gathering and search process and employ AI selectively in operational workflows.
- Heavy AI adopters: Industries deeply integrate AI across operations and heavily relies on AI in decision-making. They look for more productive and efficient AI solutions but do not invest much in development of their own products, preferring more AI outsourcing.
- Laggards: Comparatively slow AI adoption results from industry complexity and resistance to change, but progress is ongoing. In a few industries – laggards quite a ‘loth’ AI adoption can be attributed to limited tech familiarity, cost considerations, and traditional practices (f.i. in specific areas of construction)
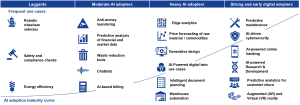
Figure 4. AI maturity curve and the most frequent use-cases of AI solutions
AI's impact on the Value Chain
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the value chain of companies across industries, reshaping the way businesses operate, deliver value, and remain competitive. Its role in the value chain is multifaceted and increasingly pivotal. At the outset of the value chain, AI contributes significantly to product design and development. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets, customer preferences, and market trends to inform product ideation. This not only enhances the innovation process but also minimizes the risk of developing products that may not meet market demands.
In the supply chain, AI optimizes logistics, inventory management, and demand forecasting. Predictive analytics, powered by AI, helps companies reduce costs, minimize waste, and ensure products are available when and where customers want them. Additionally, AI-driven robotics and automation streamline manufacturing and distribution processes. In marketing and sales, AI enables highly personalized customer experiences. Recommendation engines, chatbots, and natural language processing facilitate customer interactions and boost sales. AI-driven insights from customer data empower companies to target their marketing efforts more effectively. AI plays a crucial role in customer support and service. Chatbots and virtual assistants offer 24/7 support, resolving queries and issues promptly. Sentiment analysis helps companies gauge customer satisfaction and adapt their services accordingly. In the post-sales phase, AI enhances maintenance and support by predicting when equipment needs servicing or when products may fail. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and ensures customer satisfaction.
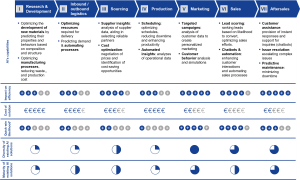
Figure 5. AI’s impact on the Value Chain phases
AI improves the efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness of support activities in the value chain. It enables companies to better manage their resources, reduce risks, and deliver higher-quality products and services to customers.
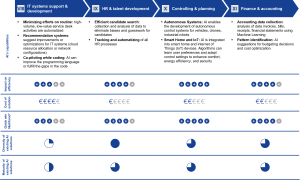
Figure 6. AI’s impact on the Value Chain phases (Support actitivies)
In essence, AI is an integral part of the modern business value chain, driving efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness. Its impact will continue to expand as companies leverage its capabilities to create value and meet evolving customer expectations.
Case Studies about the AI's influence on efficiency in the Value Chain
AI fosters Cost-saving potential in each phase of Value Chain in manufacturing. Each phase can be assessed with capabilities of existing AI solutions or approaches and the cost of AI adoption differs (routine functions can be easily automated with AI but complex processes are not). Each phase also is different in terms of chance to get a quick win after AI implementation. There are many use-cases already heavily integrated in the business operations, both internally developed and specifically designed by technological companies for purpose of outsourcing.

Figure 8. AI in inbound/ outbound logistics
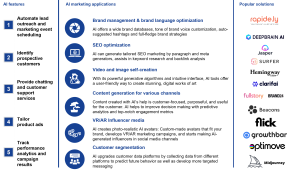
Figure 9. AI in marketing
For more use-cases download our Dossier “Driving efficiency of the value chain via the support of AI“.
Challenges and Pitfalls of AI Adoption
The S-curve of AI adoption represents the pattern of how a new technology, in this case, artificial intelligence (AI), is adopted and integrated into various industries and sectors over time. It typically follows an “S” shape when plotted on a graph. Here’s an explanation of the key phases:
- Initial Phase (Slow Adoption): In the early stages, AI adoption is relatively slow. Organizations are cautious, and there is limited awareness and understanding of AI’s potential. Pilot projects and research are common, but widespread implementation is rare.
- Acceleration Phase (Rapid Adoption): As AI technologies mature, their adoption accelerates. Companies start to recognize the competitive advantages and efficiencies AI can offer. Investments in AI increase, leading to the development of AI applications, tools, and platforms.
- Inflection Point (Steep Growth): At this stage, AI adoption reaches a critical mass. More industries and businesses embrace AI across various functions, from marketing and customer service to operations and decision-making. AI becomes a strategic priority.
- Maturity Phase (Slower Growth): After the initial rapid growth, AI adoption may slow down in certain areas as the technology matures and saturates some markets. However, new use cases and industries continue to adopt AI, ensuring ongoing growth.
- Plateau Phase (Saturation): In the final phase, AI adoption approaches saturation in many sectors, and the technology becomes ubiquitous. Most businesses have integrated AI into their operations, and innovation shifts towards optimizing and refining existing AI applications.
It’s important to note that different industries and regions may be at different stages of the S-curve, and the curve itself can vary based on the specific AI technologies and applications. The S-curve of AI adoption reflects the typical trajectory of how transformative technologies are assimilated into society and business, ultimately reshaping industries and economies.
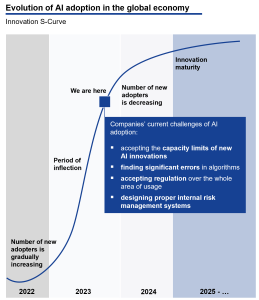
Figure 10. Timeline of AI adoption S-Curve
What should we take into account while adopting AI?
- AI solution legislation: The AI Act defines dos and don’ts for AI practices. Even if the Act is in the final negotiations phase and will be in force since 2025, AI developers should be aware of the potential legal framework to reduce future regulatory risks.
- Strict risk management: Companies fear AI’s impact, see the need for internal risk policy and legal clarity. There are many social and economic aspects to keep in mind while working with AI.
- Resource usage: AI uses massive amount of electricity and network load, as well as requires many highly-qualified specialists with deep knowledge of mathematics and economics.
FOSTEC & Company approach of strategically incorporating AI into your business operations
FOSTEC & Company provides the clients with the full-fledge process of AI adoption from stating business requirements and assessment of data and operation readiness to AI. After successful implementation the client may need regular AI health check: does AI bring the promised gains or reduce substantial costs or should be replaced with other solutions.
In each phase of the client’s Value Chain FOSTEC can help to smooth AI integration and provide the top-management with strategically tailored action list. FOSTEC approach is subject to adjust to business requirements stated by the clients. The client and the Consultant team together create the vision of a future AI-powered process.
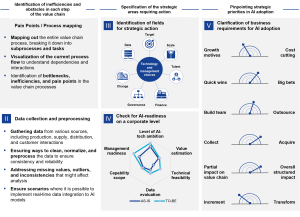
Figure 11. Our project approach: AI in your Value Chain. Comprehensive proof-of-concept aid for businesses
The outstanding product which has already been implemented with one of our clients is AI Content Powerhouse. FOSTEC & Company provides the clients with AI-Powered Content Automation for enhanced Marketing impact. It solves many efficiencies within the processes of marketing in the company significantly saving time and costs.
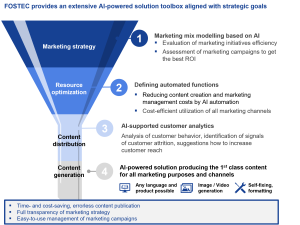
Figure 12. F&C AI Content Powerhouse
Other opportunities that you can get with F&C assistance can be learnt from our Dossier “Elevating the Value Chain through AI-driven solutions”.
Contact us and download our Dossier

Markus Fost, MBA, is an expert in e-commerce, online business models and digital transformation, with broad experience in the fields of strategy, organisation, corporate finance and operational restructuring.
Learn moreMarkus Fost
Download our service portfolio & service approach of FOSTEC & Company Driving efficiency of the value chain via the support of AI
Please provide your name and e-mail address to receive an e-mail with the according PDF file free of charge.








